Difference between revisions of "Adding a Light"
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
In the real world, each object has a different reaction to light. Steel objects are often shinier than a clay vase for example and a wooden container doesn't react the same to light as a steel container. Some objects reflect the light without much scattering resulting in small specular highlights and others scatter a lot giving the highlight a larger radius. | In the real world, each object has a different reaction to light. Steel objects are often shinier than a clay vase for example and a wooden container doesn't react the same to light as a steel container. Some objects reflect the light without much scattering resulting in small specular highlights and others scatter a lot giving the highlight a larger radius. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
The ambient material defines what color the surface reflects under ambient lighting; this is usually the same as the surface's color. The diffuse material defines the color of the surface under diffuse lighting. The diffuse color is (just like ambient lighting) set to the desired surface's color. The specular sets the color of the specular highlight on the surface (or possibly even reflect a surface-specific color). Lastly, the shininess impacts the scattering/radius of the specular highlight. | The ambient material defines what color the surface reflects under ambient lighting; this is usually the same as the surface's color. The diffuse material defines the color of the surface under diffuse lighting. The diffuse color is (just like ambient lighting) set to the desired surface's color. The specular sets the color of the specular highlight on the surface (or possibly even reflect a surface-specific color). Lastly, the shininess impacts the scattering/radius of the specular highlight. | ||
Example materials settings: http://devernay.free.fr/cours/opengl/materials.html | Example materials settings: http://devernay.free.fr/cours/opengl/materials.html | ||
Revision as of 13:05, 7 April 2021
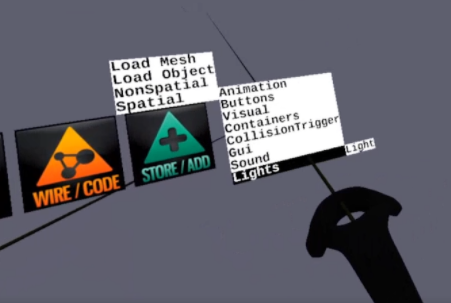
Adding a light
Choose Spatial -> Lights -> light
Type of Light
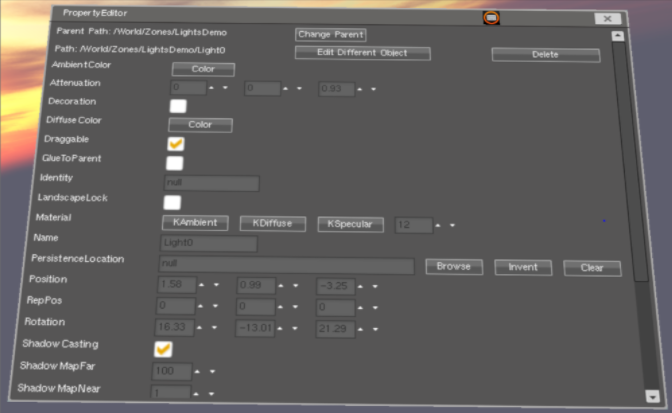
In the Property Editor for the light, you can choose 4 different types of lights (the default is a spotlight) and set the color and intensity (attenuation) and aimed direction (rotation) of a light
SPOT - shines a cone of light in a specific direction. You can specify the radius of the cone. Its intensity fades out (falloff) over distance. Adjust the amount of falloff with the third Attenuation value (set this by entering a value between 0 and 1)
Set the AmbientColor to 0,0,0 so that only the cone of light is illuminated.
DiffuseColor sets the color of the cone of light.
POINT - shines in all directions, from its location, like a light bulb. Same falloff as a spotlight.
DIRECTIONAL - shines parallel rays like the sun. It does not fade out over distance
AMBIENT - illuminates from all directions, sort of like from the sky acts like a huge light. It does not fade out over distance.
Color of light
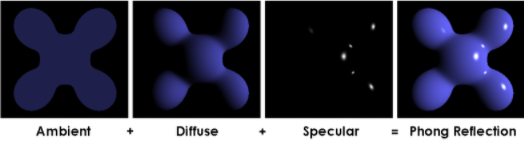
- Ambient lighting: even when it is dark there is usually still some light somewhere in the world (the moon, a distant light) so objects are almost never completely dark. To simulate this we use an ambient lighting constant that always has the object reflecting some color.
- Diffuse lighting: simulates the directional impact a light object has on an object. This is the most visually significant component of the lighting model. The more a part of an object faces the light source, the brighter it becomes.
- Specular lighting: simulates the bright spot of a light that appears on shiny objects. Specular highlights are more inclined to the color of the light than the color of the object.
The ambient light is usually set to a low intensity because we don't want the ambient color to be too dominant. The diffuse component of a light source is usually set to the exact color we'd like a light to have; often a bright white color. The specular component is usually kept shining at full intensity. All three combine to become Phong reflection
Color of materials
In the real world, each object has a different reaction to light. Steel objects are often shinier than a clay vase for example and a wooden container doesn't react the same to light as a steel container. Some objects reflect the light without much scattering resulting in small specular highlights and others scatter a lot giving the highlight a larger radius.
The ambient material defines what color the surface reflects under ambient lighting; this is usually the same as the surface's color. The diffuse material defines the color of the surface under diffuse lighting. The diffuse color is (just like ambient lighting) set to the desired surface's color. The specular sets the color of the specular highlight on the surface (or possibly even reflect a surface-specific color). Lastly, the shininess impacts the scattering/radius of the specular highlight. Example materials settings: http://devernay.free.fr/cours/opengl/materials.html